| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Rake/Trail |
Rake is the angle the steering is inclined from the
vertical. Trail is the distance between an imaginary line drawn
vertically through the wheel axle and an imaginary line drawn through
the steering head. The distance between these two lines when they meet
the floor is the trail. (perhaps it would be easier to use a diagram) |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Bore x stroke |
Bore is the internal diameter of the cylinder. Stroke is the distance
the piston travels from the bottom to the top of the cylinder. Both are
measured in millimetres |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
KIPS®
KIPS-D |
Kawasaki
Integrated Power Valve System (KIPS®)
KIPS system varies exhaust port height for
increased horsepower and torque Produces a broad power band with more low-end
torque while retaining excellent top-end power. KIPS-D the same as
above with
automatic Decompression system. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
K-TRIC |
Kawasaki Throttle Responsive Ignition Control (K-TRIC). By utilizing the
Digital Ignition system and a throttle-position sensor on the
carburettors, K-TRIC varies timing according to throttle position and
engine rpm so the ignition compensates for differing engine loads. The
result is crisp throttle response and optimum fuel efficiency.
|
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
KACR |
Kawasaki Automatic
Compression Release (KACR) system and hot start circuit. KACR slightly
opens one exhaust valve while the engine is being kick started to ease
compression. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
KLEEN / KCA |
KLEEN (Kawasaki
Low Exhaust Emission) System, Helps keep exhaust emissions
environmentally friendly. Reductions in exhaust emissions also aided by
reshaping the guide for the secondary air reed valve. KCA (Kawasaki
Clean Air) system routes fresh air to the exhaust ports for cleaner
exhaust emissions.
It's a system that
connects the exhaust valves to the airbox via reed valves, which sucks
clean air into the exhaust pipes during the exhaust stroke to help
ignite any unburned fuel from the power stroke |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
SOHC, DOHC,OHV |
Single Over Head Camshaft, Double Over
Head Camshaft, Over Head Camshaft. |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
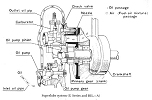
SUPERLUBE |
Superlube oil injection system eliminates mixing
fuel and oil, a common procedure with many two-stroke engines, and
delivers the precise amount of lubrication to the engine for greater
reliability and reduced emissions |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
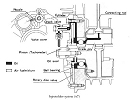
INJECTORLUBE |
Autolube and
Injectolube are different brand names for the same thing. In the
Injectolube system the crankshaft-driven oil pump was retained
along with the throttle control. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
AVDS |
Automatic Variable Damping System, for
increasing compression damping, witch works automatically and provides
more damping as fork travel and speed of fork increase. There is a
spring loaded valve on top of the damper rod in each fork, when about
one third of the fork travel is used, the main fork spring forces the
valve shut. As the fork continues to compress, pressure increases inside
the damper rod, underneath the valve, eventually building high enough to
progressively force the valve open, allowing the fork to compress
slowly. Spike loads created by big bumps knock the spring loaded valve
off and allow the fork to react.
The system was first used on the
GPZ900R and GPZ750R back in 1984. source: Cycle World |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Page last updated:
søndag, 05. juni 2016 |
|
|
